How Modern Circular Knitting Machines Transform Polar Fleece Manufacturing
Nov 18, 2025
Polar fleece has become one of the most widely used textile materials in the global apparel and home furnishing industries due to its exceptional warmth, durability, and versatility. From winter jackets and sportswear to blankets, gloves, and outdoor gear, fleece fabric has earned its place as a staple in both consumer and industrial applications. Its production, however, is far more technologically sophisticated than many expect. Modern fleece manufacturing relies on advanced circular knitting machines, specialized finishing equipment, and highly controlled production techniques to deliver fabrics that meet stringent standards for quality, performance, and consistency.
This news feature takes a deep dive into the world of polar fleece: what it is, how it is made, how it is classified, and why circular knitting machines play such an essential role in ensuring consistent fabric quality. It also explores the mechanical innovations of today’s fleece circular knitting machines and how they have modernized textile production for manufacturers worldwide.
Polar fleece—often simply called “fleece”—is a knitted fabric recognized for its soft texture, impressive thermal insulation, and lightweight feel. Contrary to natural wool or cashmere, fleece is typically made from synthetic fibers such as polyester, offering a cost-effective yet high-performance alternative.
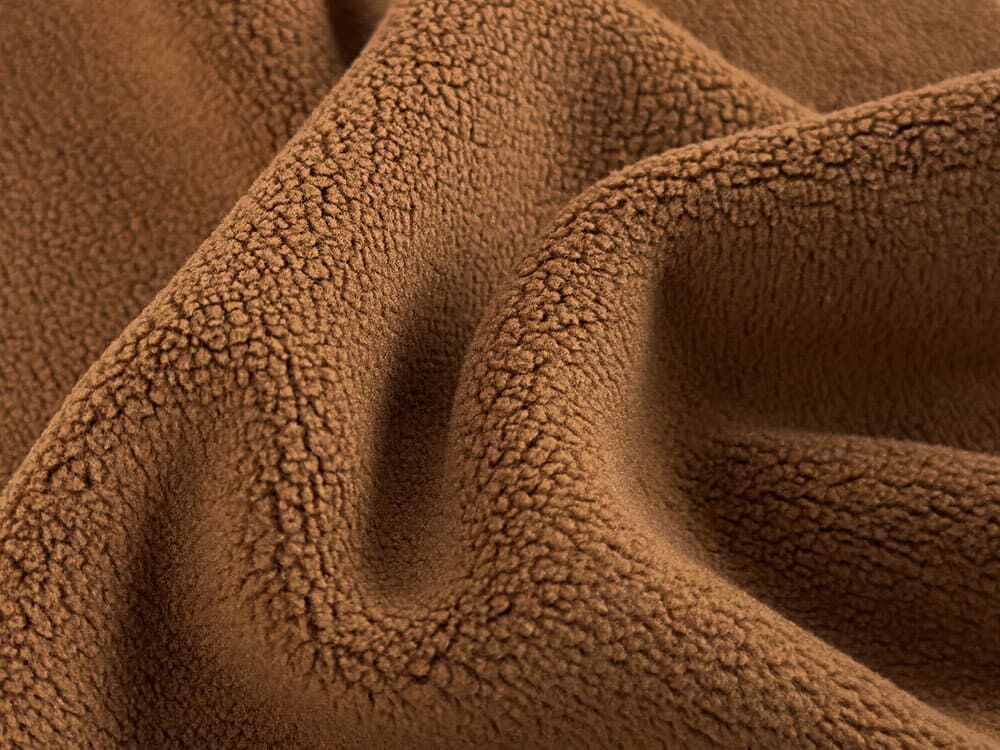

The production process begins with circular knitting, where polyester yarn is knitted into grey fabric using a large-diameter circular knitting machine. Once the knitting stage is complete, the fabric undergoes a series of finishing treatments:
Dyeing – The grey fabric is dyed to achieve the desired color.
Raising – Machines use fine needles to pull up fibers on the fabric surface, creating a soft pile.
Carding – Loose fibers are combed to align and refine the pile.
Shearing – The raised surface is trimmed to ensure uniform height and smoothness.
Shaking/Finishing – High-speed equipment fluffs the fabric to produce the signature fleece texture.
The result is a fabric that is warm, soft, lightweight, and resistant to pilling. The front surface typically features a full, dense, and fluffy pile, while the reverse side is lightly raised, offering elasticity and clarity in texture.
Polar fleece is valued for its combination of comfort, function, and adaptability. Its most notable characteristics include:
Soft and Comfortable: The fiber density and raised pile provide a plush feel against the skin.
Excellent Insulation: Trapped air within the pile makes fleece highly effective at retaining heat.
Durable and Anti-Pilling: Proper finishing improves surface stability, preventing shedding.
Lightweight and Breathable: Despite its warmth, fleece remains light and suitable for athletic applications.
Easy to Combine: Fleece can be laminated or bonded with various materials—such as denim, lamb fleece, mesh fabrics, or waterproof breathable films—to enhance functionality.
Its versatility makes it suitable for both casual wear and technical apparel.
Fleece can be categorized in several different ways depending on the raw materials used, the processing methods applied, and the final product’s style or purpose. Understanding these classifications is essential for textile manufacturers, apparel designers, and buyers aiming to select the right type of fleece for specific end uses.
Produced using short polyester fibers, this type of fleece offers a stable pile, soft texture, and superior warmth. Because staple fibers are more complex to process and require higher precision in raising and carding, the cost is typically higher than long-fiber fleece.
Manufactured using long, continuous polyester filaments such as DTY (Draw Textured Yarn) or FDY (Fully Drawn Yarn). This version tends to be smoother, shinier, and more suitable for blankets or lightweight garments. Long-fiber fleece usually costs less than staple-fiber fleece due to its simpler processing requirements.
A standard treatment where the fabric is raised once and then shaken to form a soft, even pile.
Offers a thicker, fluffier, and more luxurious fabric with enhanced warmth retention.
Provides a balance between volume and cost, offering warmth without overly increasing fabric density.
Often used for bonded or laminated fabrics, combining fleece with other materials.
A specialized finishing method that improves dimensional stability and texture.
Simple and widely used in apparel, accessories, and home textiles.
Striped fleece used in fashion garments and decorative applications.
Plaid or patterned fleece providing visual interest and stylistic appeal.
The widespread use of fleece highlights its adaptability across industries. Some of the most common applications include:
Fashion and Apparel: Jackets, coats, vests, hoodies, windbreakers, and sportswear.
Outdoor and Technical Gear: Hiking gear, thermal wear, gloves, hats, scarves.
Home Textiles: Blankets, carpets, pillowcases, cushions, bedding.
Branding and Accessories: Clothing logos, embroidered patches, shoe linings.
Toys and Crafts: Soft toys and creative DIY materials.
The most commonly referenced material configuration in industrial use is full polyester 150D/96F fleece, where “D” refers to yarn thickness and “F” indicates the number of filaments.
At the heart of polar fleece manufacturing lies the circular knitting machine. These machines determine the structure, density, and uniformity of the fleece base fabric before it even enters the finishing stage. As global demand for high-quality fleece continues to grow, manufacturers are increasingly turning to advanced circular knitting machines designed specifically for fleece production.
Modern machines deliver higher precision, stability, and efficiency, ensuring consistent quality across large production batches. Their innovations directly influence yarn feeding, loop formation, and surface uniformity—key factors in fleece performance.
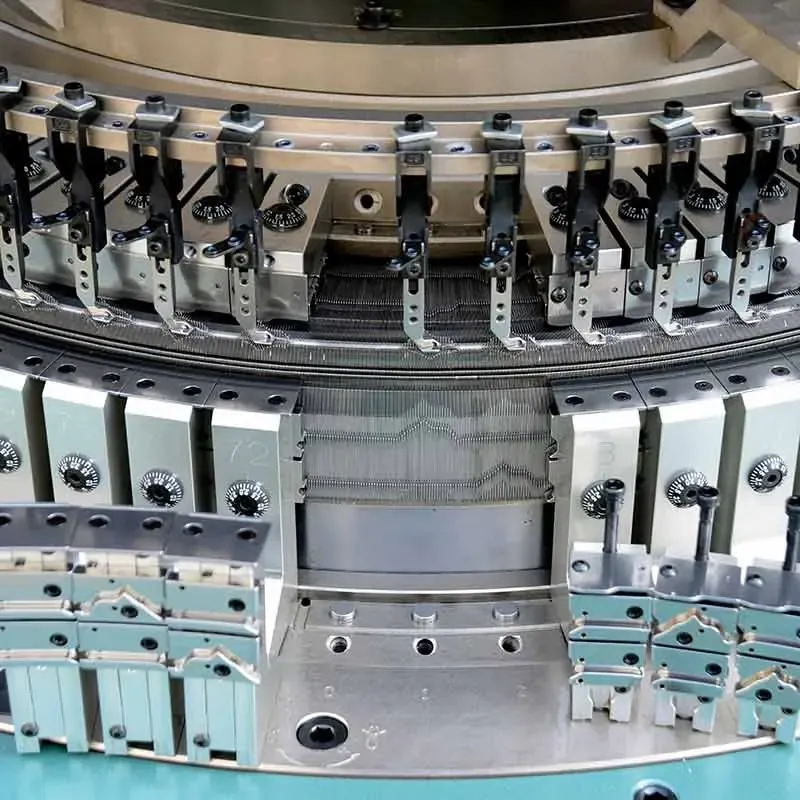
Industry-leading fleece knitting machines integrate multiple engineering advancements that improve productivity, fabric consistency, and machine life span. Below are the core features and benefits that define today’s high-performance fleece circular knitting machines.
This innovative bearing structure enhances machine running precision and reduces impact resistance. By minimizing mechanical friction, the machine operates more smoothly, ensuring stable loop formation and improved knitting accuracy.
In addition, the suspended design significantly lowers energy consumption during the drive process, making production more efficient and environmentally sustainable.
Critical components of the machine, such as the cam box, are made using aircraft aluminum alloy. This material provides:
Superior heat dissipation
Reduced weight and lower inertia
High resistance to deformation
Improved long-term stability under load
These properties help maintain precise machine operation even under continuous high-speed production.
Traditional manual visual inspection introduces human error into stitch adjustments. Modern fleece circular knitting machines feature a precision-engineered one-stitch adjustment mechanism that replaces visual estimation with mechanical accuracy.
The system uses Archimedean adjustment principles, offering:
High-precision calibration
Accurate scale display
Simplified replication of the same fabric on multiple machines
Faster and more reliable setup for repeat orders
This greatly benefits factories running high-volume or multi-machine production lines.
A uniquely designed machine body provides superior structural rigidity compared to traditional designs. This reduces vibration, enhances operational stability, and extends the life of machine components—all critical factors for long-term, high-speed fleece production.
The central stitch system simplifies machine operation by providing:
Higher adjustment accuracy
A more intuitive control mechanism
A streamlined internal structure
Faster learning curve for operators
This makes daily production more efficient and reduces downtime during stitch changes or fabric transitions.
Sinker plates are essential in loop formation and fabric control. Deformation in traditional sinker plates can reduce knitting precision and cause fabric defects.
Modern fleece machines feature a redesigned sinker plate fixing system that:
Eliminates deformation
Enhances edge stability
Reduces maintenance frequency
Improves overall knitting accuracy
This improvement contributes to more uniform fabric output and minimizes product defects.
The global demand for polar fleece continues to increase due to rising interest in outdoor activities, higher consumption of winter apparel, and the growing prominence of athleisure wear. Markets such as North America, Europe, and East Asia remain strong consumers, but emerging markets are also accelerating growth.
Key industry trends include:
Sustainable Fleece: Manufacturers increasingly use recycled polyester (rPET) derived from plastic bottles.
Bonded and Composite Fleece: Hybrid materials combining fleece with waterproof films or softshell fabrics are gaining popularity.
Smart Knitting Machinery: Automation and digital controls enable more stable production and fewer fabric defects.
Customization Needs: Fashion brands demand more textured, patterned, and color-rich fleece varieties.
Circular knitting machine manufacturers are responding by upgrading machine compatibility with recycled fibers, improving digital control systems, and offering greater flexibility for diversified fleece styles.
Polar fleece remains one of the most influential textile materials in the modern apparel and home furnishing industries. Its warmth, softness, durability, and adaptability make it a cornerstone of winter clothing, outdoor gear, and countless everyday products. Behind this remarkable fabric is the essential role of circular knitting machines, which provide the precision, consistency, and production efficiency needed to meet global demand.
With continuous advancements in machine design—such as suspended wire race bearings, aircraft aluminum components, precision stitch systems, and improved structural stability—textile manufacturers can achieve higher output, better fabric quality, and increased competitiveness.
As the market evolves, fleece production technologies will continue to innovate, supporting a wide range of applications from high-performance sportswear to eco-friendly textiles. For buyers, manufacturers, and industry professionals, understanding the intricate process of fleece production and the machinery behind it is key to staying ahead in an increasingly competitive textile landscape.
Previous: How Circular Knitting Machines Are Revolutionizing Technical Textile Production
We have been committed to manufacturing all types of circular knitting machines with great quality and reasonable price for a long time. Our professional team is highly specialized and problem-solving oriented. We put the most effort into meeting your knitting demands, achieving a win-win situation.