Essential Maintenance Tips for Beginners Using Circular Knitting Machines
Oct 02, 2025
Circular knitting machines are the backbone of modern textile production, playing a pivotal role in manufacturing garments that millions of people wear every day. From cozy sweaters to comfortable socks and everyday t-shirts, these machines help create high-quality knitted fabrics efficiently and consistently. Yet, for beginners stepping into the world of textile machinery, understanding how to maintain circular knitting machines can be a daunting task. Without proper care, even the most advanced machines can experience breakdowns, reduced efficiency, or compromised fabric quality.
This article offers a comprehensive guide for beginners, providing essential maintenance tips to ensure that circular knitting machines remain in top working condition, extend their lifespan, and produce high-quality knitted fabrics with minimal downtime.
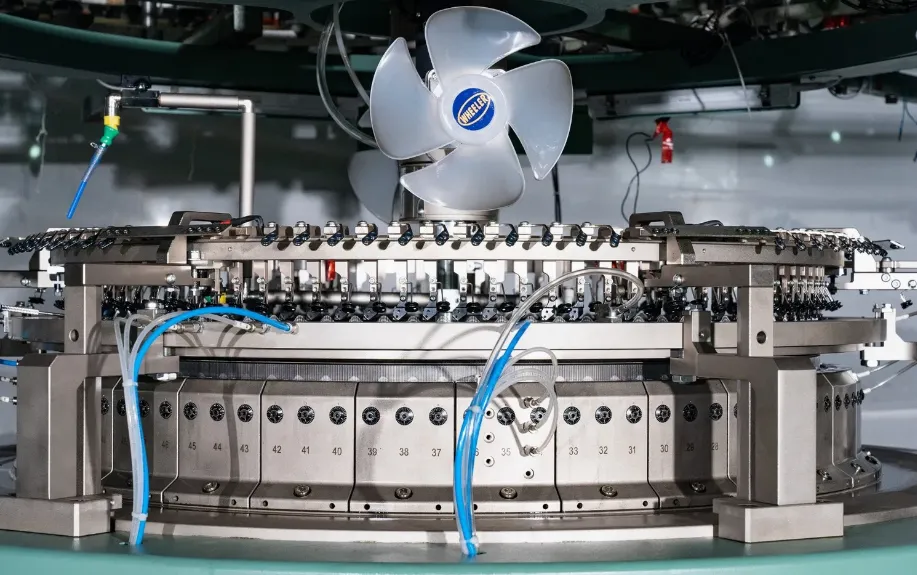
A circular knitting machine is designed to produce tubular knitted fabrics using a rotating needle bed arranged in a circular formation. Unlike flat knitting machines that create rectangular fabrics, circular knitting machines allow continuous, seamless production, making them highly efficient for both small and large-scale textile operations.
To understand maintenance requirements, it is helpful to familiarize yourself with the main parts of a circular knitting machine:
Needle Beds: The rotating bed where needles are mounted. These are essential for creating the loops that form the fabric.
Needles and Sinkers: Critical elements that manipulate the yarn to produce knitted loops. Needles move vertically while sinkers guide and hold the loops.
Yarn Feeding System: Supplies yarn consistently to the needles, ensuring uniform tension and fabric quality.
Tension Discs: Control the tightness of the yarn to prevent loose or overly tight knitting.
Motor and Drive System: Powers the rotation of the needle beds and overall operation.
Machines come in various sizes depending on the type of fabric being produced. Smaller machines are ideal for socks, cuffs, or sleeves, while larger machines accommodate full garments and high-volume production.
Routine maintenance is essential for several reasons:
Longevity: Regular care significantly extends the machine's operational life.
Fabric Quality: Machines in poor condition can cause uneven stitching, broken yarns, or tension issues.
Efficiency: Well-maintained machines operate smoothly, reducing downtime and production delays.
Safety: Ensuring components function correctly prevents accidents in the workplace.
For beginners, understanding the importance of each maintenance step can make machine care less intimidating and more systematic.
Daily upkeep is the first and most important line of defense against machine issues. Consistent attention helps prevent minor problems from escalating into major failures.
Dust, lint, and yarn residue can accumulate quickly during operation. Left unchecked, these can hinder machine performance or even cause mechanical damage. Beginners should:
Use a soft brush or air compressor to remove debris from needle beds, sinkers, and yarn feeders.
Wipe external and internal surfaces with a clean, lint-free cloth.
Avoid using excessive moisture or harsh chemicals that could damage delicate components.
Friction between moving parts accelerates wear and can lead to costly replacements. Proper lubrication ensures smooth movement and reduces the risk of overheating. Tips for effective lubrication include:
Apply the manufacturer-recommended oil or grease to the needle beds, sinkers, and moving components.
Avoid over-lubrication, which can attract dust and dirt.
Monitor lubrication levels daily and replenish as needed.
Correct yarn tension is crucial for consistent fabric quality. Improper tension can cause loops to be too loose or too tight, affecting the finished product. Beginners should:
Inspect yarn tension discs for smooth operation.
Adjust tension according to fabric type and yarn specifications.
Test fabric samples after adjustments to ensure even knitting.
Circular knitting machines generate heat during operation, particularly during prolonged use. Overheating can damage components or reduce performance. Preventive measures include:
Operating the machine in a well-ventilated area.
Avoiding long continuous use without breaks.
Allowing the machine to cool periodically, especially during high-speed operation.
Electrical safety is a critical consideration. Faulty power cords or inconsistent voltage can damage machines or pose hazards. Beginners should:
Inspect cords for wear, cracks, or exposed wiring.
Ensure proper grounding and voltage supply according to the machine’s specifications.
Replace damaged cords immediately to prevent accidents.
Safety should never be overlooked, even for routine tasks. Beginners should:
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and ear protection.
Keep loose clothing and hair away from moving parts.
Be vigilant when operating machines, especially when troubleshooting or performing adjustments.
While daily care keeps the machine operational, weekly maintenance ensures that all systems are functioning optimally.
Deep Cleaning: Remove more persistent dust, fibers, and grease buildup from hard-to-reach areas.
Needle and Sinker Inspection: Check for bent or damaged needles, worn sinkers, or missing components. Replace immediately if needed.
Tension Verification: Conduct thorough tension tests to prevent quality issues in upcoming production runs.
Lubrication Audit: Review the machine’s lubrication system, ensuring oil or grease distribution is uniform.
Component Alignment: Check the alignment of needle beds, yarn feeders, and sinkers for smooth operation.
Monthly maintenance focuses on in-depth inspections and preventive replacement of components. This level of care ensures machines remain reliable for long-term production.
Comprehensive Inspection: Examine every mechanical and electrical part for signs of wear or malfunction.
Replacement of Worn Components: Even minor wear on needles, sinkers, or tension discs can affect performance. Replace them as needed.
Motor and Drive System Maintenance: Inspect belts, gears, and motors. Clean, lubricate, and adjust as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Calibration: Ensure the machine is correctly calibrated for accurate knitting, avoiding potential defects in fabrics.
Beyond daily, weekly, and monthly routines, some additional practices can simplify maintenance and improve outcomes.
Keeping a maintenance log is invaluable. Record:
Cleaning and lubrication dates.
Parts replaced or repaired.
Issues observed and solutions applied.
This documentation aids troubleshooting, planning future maintenance, and understanding patterns in machine performance.
Investing in high-quality replacement parts ensures longer service life and optimal machine performance. Inferior components may save money initially but often lead to more frequent breakdowns and costly repairs.
Textile technology evolves rapidly. Beginners benefit from ongoing education:
Attend workshops or training sessions provided by machine manufacturers.
Follow online tutorials or guides specific to the machine model.
Consult with experienced operators for practical tips.
Every circular knitting machine has its own specific maintenance requirements. Manuals often provide guidance tailored to the model, including:
Recommended lubricants and cleaning agents.
Proper tension settings for different fabrics.
Detailed troubleshooting instructions.
Following the manual ensures safe operation and preserves warranty coverage.
Even with the best practices, beginners may face challenges. Understanding common problems helps prevent downtime:
Needle Breakage: Often caused by excessive tension or improper yarn feeding. Regular inspection and proper adjustment prevent this.
Uneven Knitting: Usually a result of incorrect tension or worn needles. Adjust tension and replace worn components.
Noise and Vibration: Can indicate lubrication issues, misalignment, or worn gears. Inspect and correct promptly.
Overheating: Caused by continuous operation without breaks or poor ventilation. Introduce cooling periods and ensure airflow.
Addressing these issues early prevents more serious mechanical failures and reduces repair costs.
To make maintenance easier, beginners can follow this simple daily routine:
Check oil levels and lubricate critical components.
Clean the machine surface and needle beds.
Verify yarn supply and tension settings.
Monitor machine performance for unusual noises or vibrations.
Observe fabric quality to catch tension or needle issues early.
Ensure the machine area remains clean and free from obstructions.
Turn off the machine and clean thoroughly.
Record any issues or part replacements in the maintenance log.
Prepare the machine for the next day, including checking electrical connections and cooling components.
For beginners in textile production, mastering circular knitting machine maintenance is crucial for long-term success. Regular care—including cleaning, lubrication, tension adjustment, inspection, and safety checks—ensures machines run smoothly, produce high-quality fabrics, and remain operational for years.
Beyond routine maintenance, keeping detailed logs, using quality replacement parts, continuous learning, and adhering to manufacturer guidelines are key strategies to minimize downtime and optimize machine performance.
Circular knitting machines may seem complex at first, but with consistent care and attention to detail, beginners can confidently operate and maintain them. By integrating daily, weekly, and monthly maintenance practices into their workflow, operators ensure that their textile machinery remains a reliable, efficient, and safe cornerstone of garment production.
Taking the time to understand and follow these maintenance tips is an investment in both your skill development and the longevity of your circular knitting machine—resulting in better fabrics, fewer breakdowns, and a smoother, more rewarding textile production process.
Next: Poly Cotton Interlock Fleece Fabric Round Knitting Machine Gains Ground in Russia’s Textile Market
Previous: Which Circular Knitting Machines Are Ideal for Double Knit Fabrics?
We have been committed to manufacturing all types of circular knitting machines with great quality and reasonable price for a long time. Our professional team is highly specialized and problem-solving oriented. We put the most effort into meeting your knitting demands, achieving a win-win situation.